- Compact, water pressure-tight design
- Reduced energy costs
- Shorter mixing times
- Minimal risk of motor overloading
- Easy installation
- Small space requirements
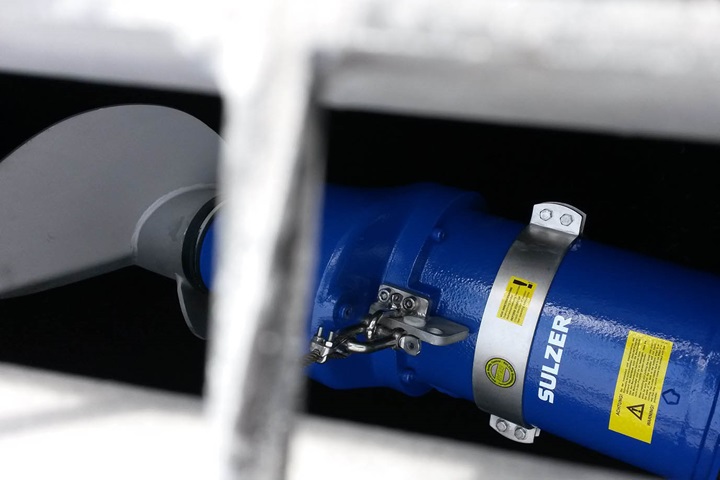
Submersible mixer type ABS RW
Compact, versatile submersible mixers
The RW is Sulzer’s standard range of submersible mixers, economical without compromising on reliable design. These compact, versatile submersible mixers are ideal for agitating, blending, mixing, dissolving, and suspension of solids in municipal treatment plants, industry, and agriculture. The RW mixers can easily be fitted to existing guiderails and lifting devices without modification, using our wide range of brackets and adapters.
- Mixing and stirring applications in sewage treatment plants and industrial areas
- Homogenization of highly-concentrated sludge and slurries
- Hazardous locations ATEX (Ex II 2G Ex h db IIB T4 Gb), FM and CSA available as an option
Main design features
- Patented solids deflection ring
- Blockage-free propeller
- Integral motors ranging from 1.3 to 13 kW (1.7 - 17.5 hp)
- RW 200 is mainly used for mixing applications in pump sumps
- Multiple and gear-driven mixers with standard or explosion-proof motor enclosures
- Support includes literature and computer software for sizing and design of each installation
Key characteristics
| Maximum mixing flow | 0,83 m³/s (14,600 US gpm) |
| Maximum propeller diameter | 650 mm (25.6 in) |
More info about the RW mixers
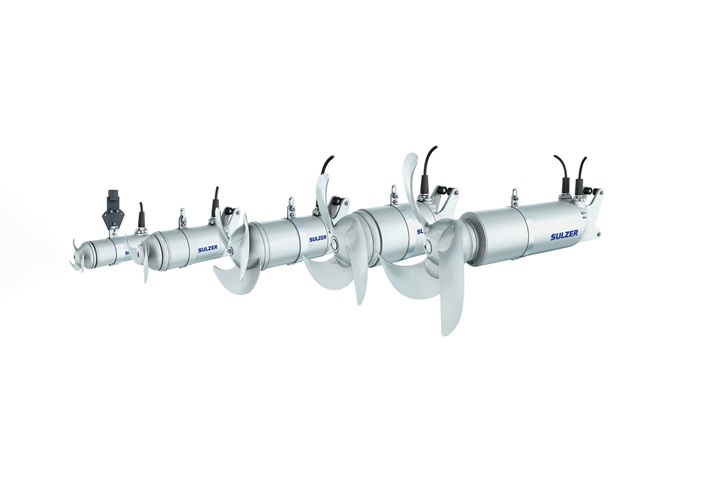
- The RW series includes several submersible mixers with integral motors ranging from 1.3 to 13 kW (1.7 - 17.5 hp) for agitating, blending, mixing, dissolving, and suspension of solids in municipal treatment plants, industry, and agriculture
- The RW 200 is mainly used for mixing applications in pump sumps
- Sulzer offers highly efficient multiple and gear-driven mixers with either standard or explosion-proof motor enclosures
- Sulzer support includes literature and computer software for sizing and design of each installation
Case studies
-
Sulzer mixers designed to tackle digested sludgeThe wastewater treatment plant of Crispijana, operated by the municipal water and sewage company Amvisa (Aguas Municipales de Vitoria-Gasteiz, S.A.), treats the wastewater from the city of Vitoria-Gasteiz, Álava, Spain. The plant has a capacity of 120’000 m³/day, 500’000 population equivalent. It has undergone a number of changes and extensions since it was opened in 1984. During the latest upgrade in 2016, the mixing problem caused by the high sludge content was solved.
-
Case studiesWherever fluids are pumped, mixed, controlled or applied, we are there. See how our solutions create value for customers and learn how we can make your pumping and mixing processes more efficient and profitable, safeguarding your production and ensuring lasting reliability.
Documents
Brochures
Case studies
Data sheets
Dimension drawings
-
Dimension Drawing Drilling Mud - RWpdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - RW 400pdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - RW 480PDFLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - RW 650pdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - RW 900pdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - RW 7511pdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - Lifting unit 2.3 kNpdfLanguages:
-
Dimension Drawing - Lifting unit 5,0 kNpdfLanguages:
Manual
Project design files BIM
Applications
-
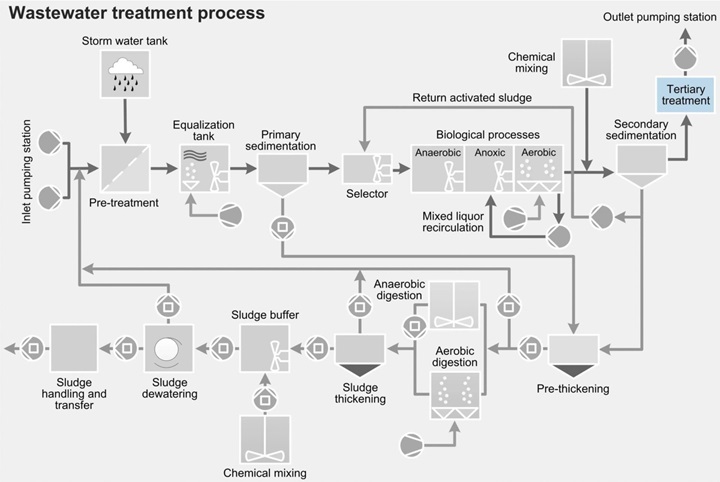
Biological processThe target of the biological process in wastewater treatment is to remove organic, biodegradable substances via the metabolism of microorganisms and related biochemical processes.
-
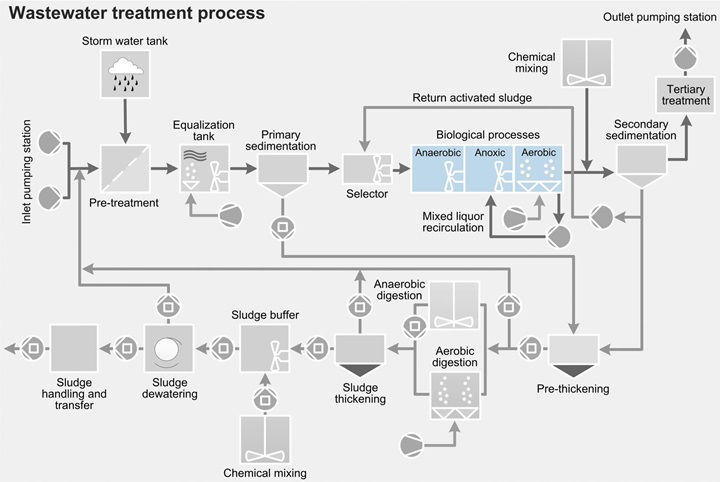
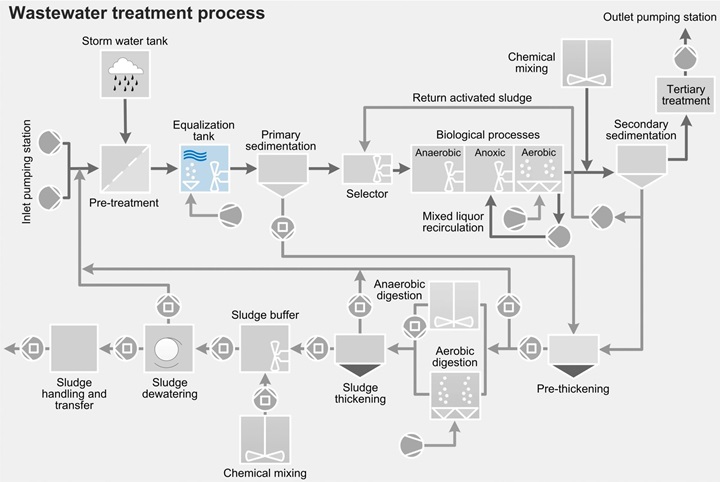
EqualizationThe task of mixing in the equalization process is to blend the wastewater in order to prevent sedimentation, stratification and odor formation. It may also be necessary to mix and homogenize wastewater streams that arrive from different sources. Because the water level in the equalization tanks varies significantly and can sometimes be very low, high demands are placed upon the mixers.
-
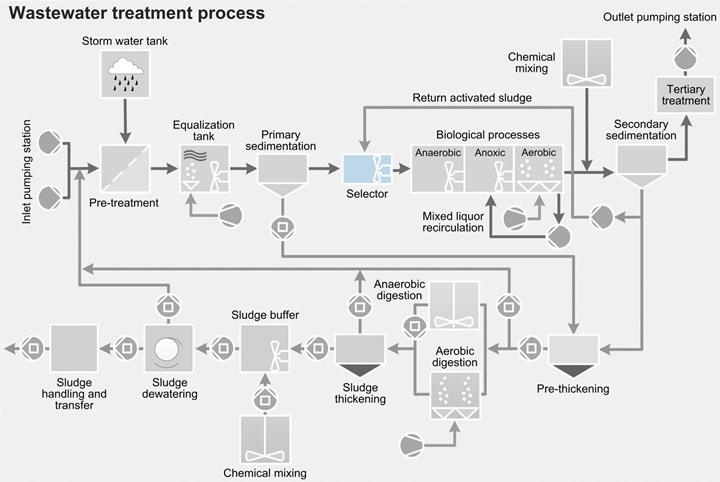
SelectorThe purpose of the selector tank is to control and limit the growth of filamentous bacteria, and then to enhance the sedimentation ability of the sludge. Sulzer provides a number of solutions for creating optimal conditions in the selector.
-
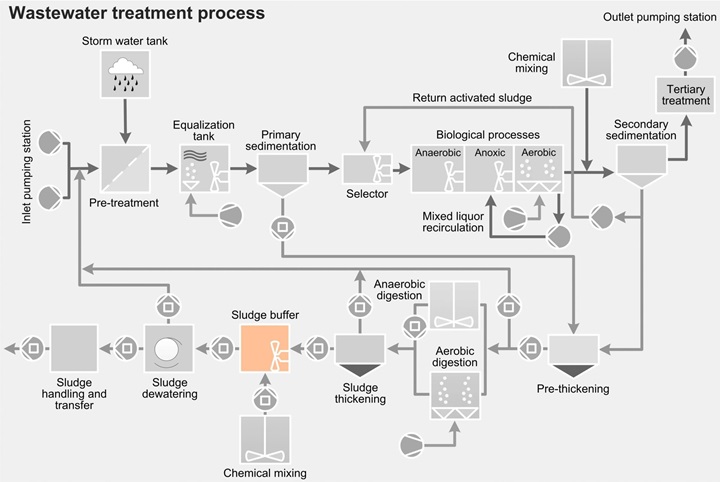
Sludge buffer tankThe sludge buffer tank can be used for a variety of purposes. The most common application is the blending and homogenization of highly concentrated primary, secondary or digested sludge. The solution used to mix the sludge itself, or to mix the sludge with the dosed thickening chemicals, depends on the design and volume of the sludge buffer tank. Submersible mixer types ABS XRW and RW, as well as the agitator type Scaba, can be used to provide highly efficient mixing. Positive displacement, progressing cavity transfer pumps and Muffin Monster™ grinders are used for solids reduction and sludge transfer from sludge feed to sludge dewatering process.
-
Tertiary treatmentTreated wastewater may occasionally require further treatment. Local discharge rules may pose strict limits that cannot be fulfilled by even the most effective process, or a higher quality of effluent may be requested for its reuse. When tertiary treatment is needed, various levels of filtration can be applied, including very fine filtration. Often, however, a final step of mixing and aeration is sufficient to achieve the target. When this is the case, Sulzer's submersible mixer types ABS XRW and RW can be used, along with submersible aerator type ABS TA–TAK and disc diffuser system types ABS PIK, DS and Sucoflow.
Talk or write to our experts to find your best solution.